Table of contents
Open Table of contents
Introduction
We all like the freshness of a newly installed linux distribution but after using it for months, after installing various programs, software stacks, tools and changing configuration files linux distro feels so stale. This was the reason I was regularly (after 6-8 months) reinstalling linux disto on my machine to get the feel of brand new install. I have distro hopped several times in the past, used different desktop environments and tiling window managers but finally I landed on Fedora Silverblue and using it for past one year. The immutable nature of Fedora Silverblue keeps the root filesystem untouched resulting in unclutered host machine forever. In this article I will be sharing how I use Fedora Silerblue for basic daily use and for development activities using distrobox, nodejs, python and podman/docker. The inspiration for blog is this video from Jorge Castro. After watching this video I understood the cloud native workflow of fedora silverblue.
What is Fedora Silverblue
i According to Fedora Silverblue docs “Fedora Silverblue is an immutable desktop operating system. It aims to be extremely stable and reliable. It also aims to be an excellent platform for developers and for those using container-focused workflows.”. The root filesystem is readonly and cannot be changed. Programs are not installed using the package manager like other linux distros. The programs are layered on top of base operating system using a tool called rpm-ostree.
rpm-ostree install <package_name>Installing packages using rpm-ostree will create a new deployment and the modified root will be available after the reboot. I will suggest only layering “system software” packages like text editor, shell etc. This reddit thread will give you a brief idea of what packages do people usually layer on top of their base silverblue install. I do not recommended layering too many packages since we will be using
- Flatpak for installing most of the applications and
- Containerized linux distro (ubuntu) using distrobox for all our development needs.
Installation of Fedora Silverblue
Skip this part if you have already installed Fedora Silverblue.
- Grab the latest image of Fedora Silverblue from https://silverblue.fedoraproject.org/download.
- You will need a empty usb stick and Balena Etcher to flash the Fedora Silverblue iso image onto usb stick.
- The process is quite simple, just select the image and usb drive then click “Flash”.
- Reboot your system and click F8 and delete button then select Bootable usb Fedora Silverblue from the boot options screen.
- The installation is straight forward just select language, keyboard layout timezone and storage space on which you want to install Fedora Silverblue.
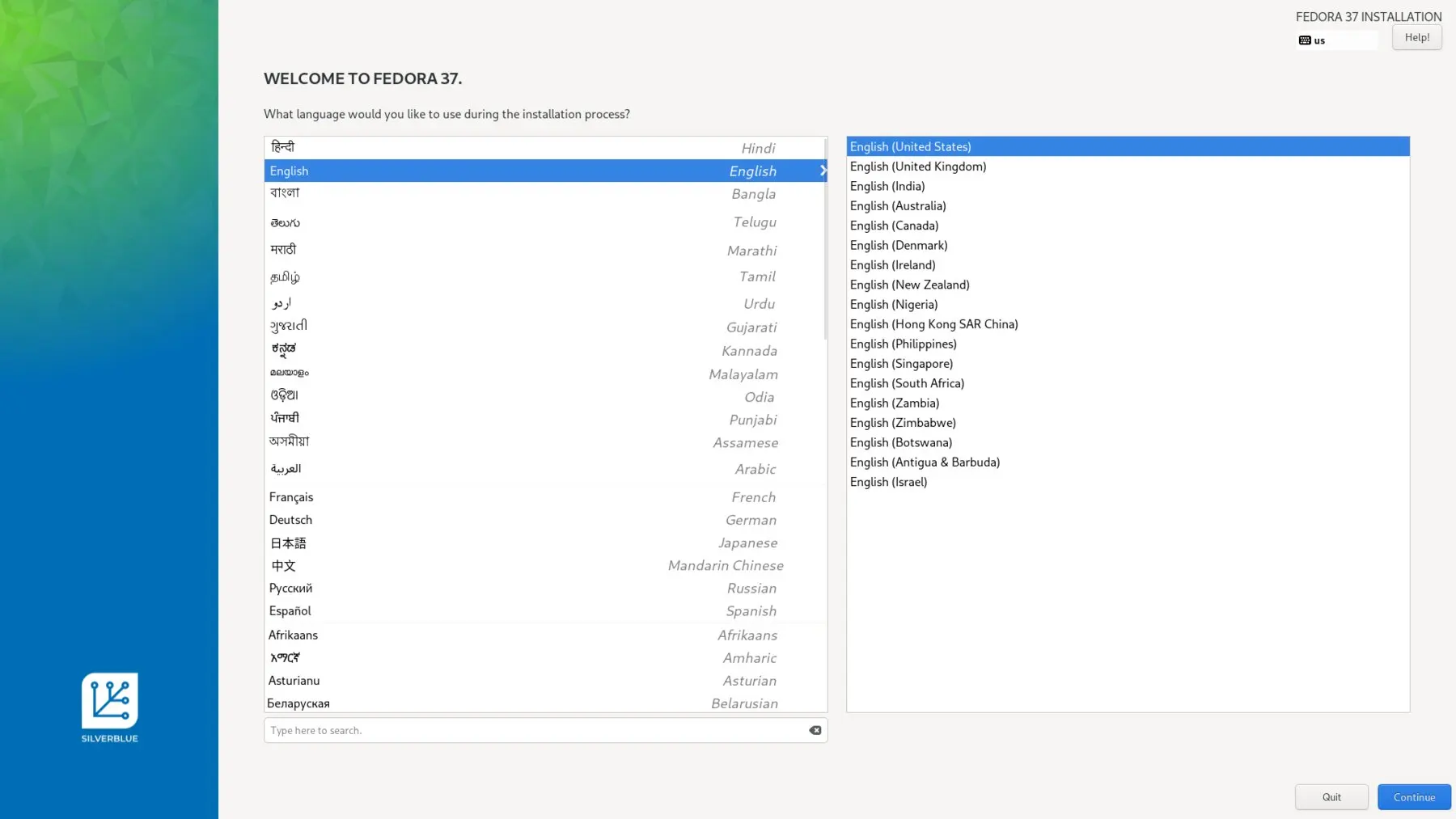
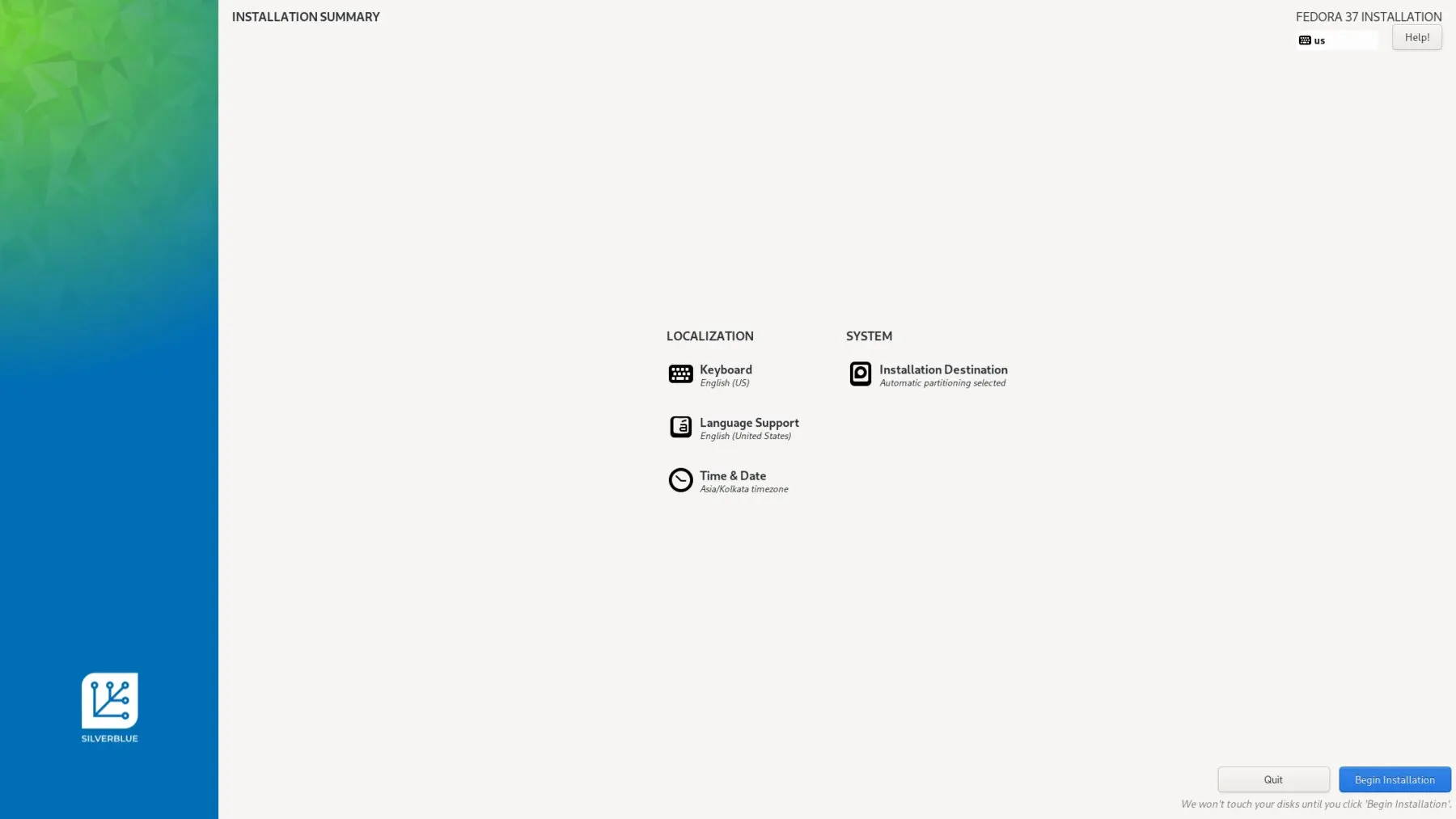
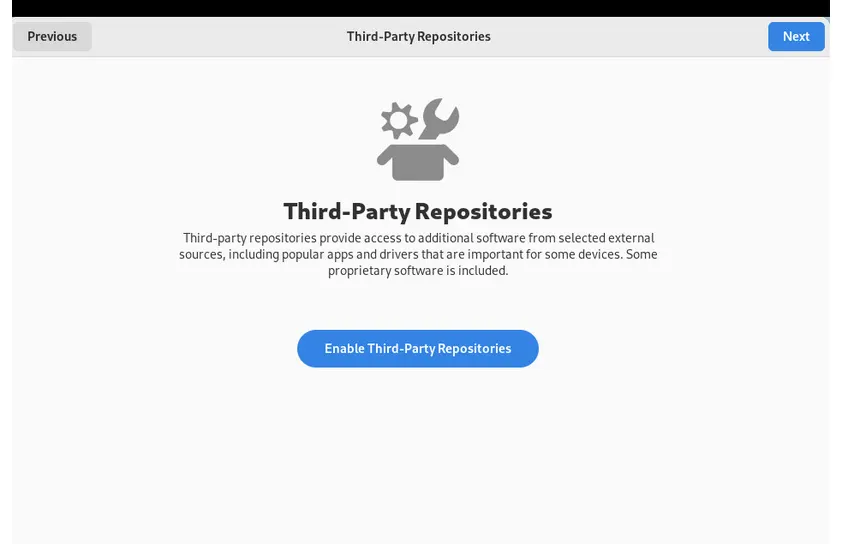
- After completion of installation complete the user creation and enable third party repositories.

Desktop Overview and workflow
Fedora Silverblue comes with latest Gnome Desktop and is identical to Fedora Workstation. How I use gnome desktop is one application per workspace and switch between workspaces using “super + 1/2/3/4”. Few changes I make to to gnome desktop that suits my workflow.
-
Switch to dark mode.
-
Setting -> Multitasking -> Disable Hot Corners
Also, In Workspaces section enable “Fixed number of workspaces” and I set Number of Workspaces to 5.
-
Changing keyboard shortcuts for managing workspaces.
Settings -> Keyboard -> View and Customize Shortcuts -> Navigation.
I do the following changes suitable for my workflow.
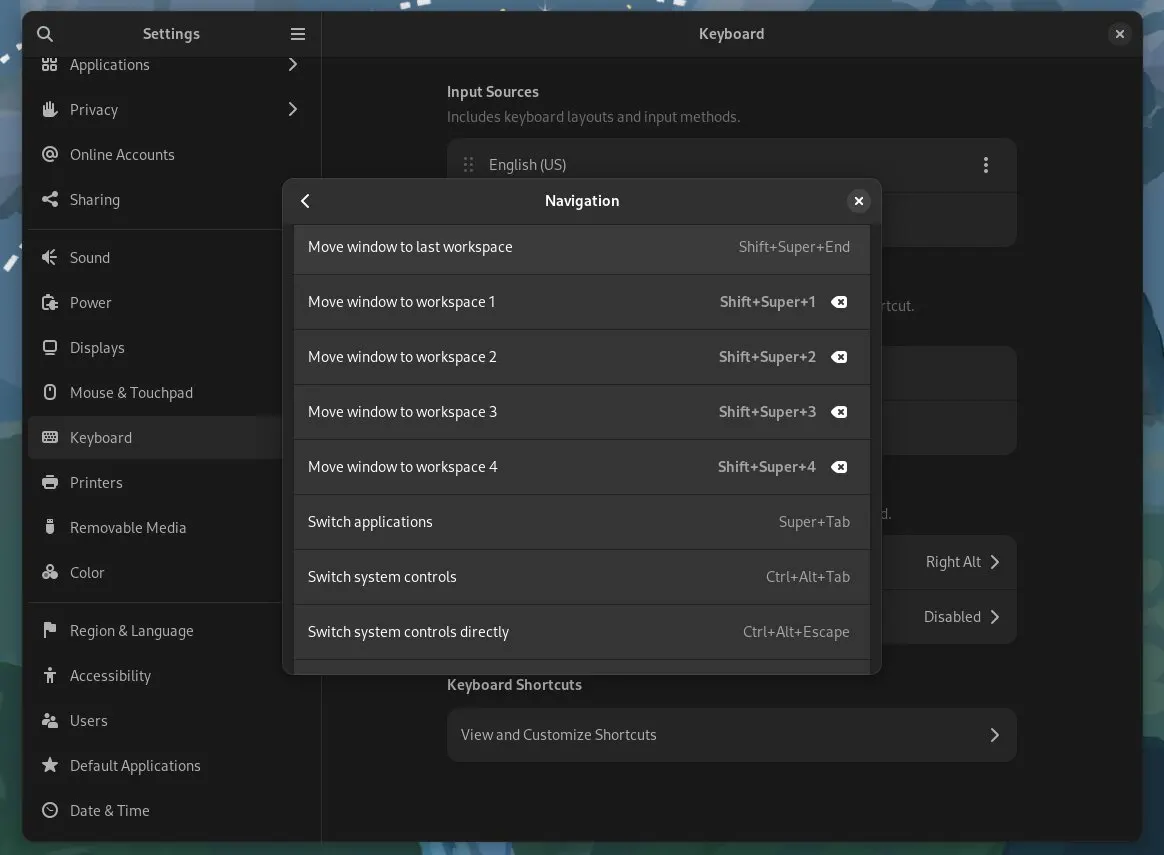
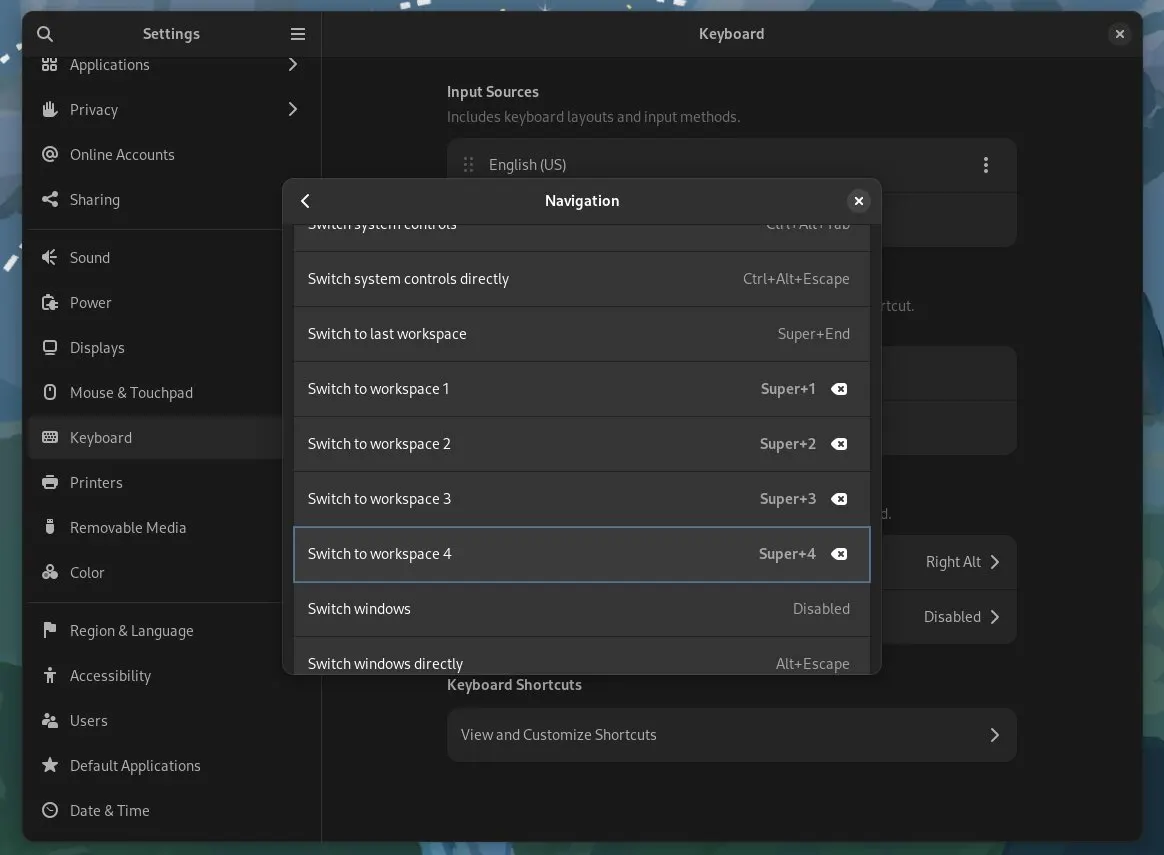
-
Settings -> Keyboard -> View and Customize Shortcuts -> Windows -> Close Window
I use Super + Q to close window.
Updates and Rollbacks
First thing to do after installing new Linux disro is updating the system.
rpm-ostree upgradeThen restart the system.
I use terminal for managing the software packages thats why I remove gnome-software and since I want to use firefox from flathub I will also delete the preinstalled firefox.
rpm-ostree override remove firefox firefox-langpacks gnome-software gnome-software-rpm-ostreeThen restart the system.
Now installing distrobox (We will work with distrobox later)
rpm-ostree install distroboxAgain restart the system for the one last time.
Everytime after making changes in the system by using rpm-ostree a new deployment is created. This allows us to rollback temporarily to previous change directly from grub menu or rollback permanently using command.
rpm-ostree rollbackYou can see your deployments using command:
rpm-ostree statusYou can pin the deployment so that it will not be garbage collected.
sudo ostree pin admin <index>Pinning current deployment
sudo ostree pin admin 0Setting up Flathub
Fedora Silverblue comes with flatpak preinstalled. It is a universal package manager on linux. Flathub is like a app store with hundreds of apps which can be installed using flatpak command. First we need to add flathub remote repository using command:
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoNow we have access to hundreds of application. Lets install firefox using flatpak flathub.
flatpak install flathub org.mozilla.firefoxFlatpaks I use are:
flatpak install flathub com.brave.Browser com.discordapp.Discord \
com.google.Chrome com.mattjakeman.ExtensionManager \
com.spotify.Client io.mpv.Mpv org.filezillaproject.Filezilla \
org.gnome.Boxes org.gnome.Cheese org.libreoffice.LibreOffice org.telegram.desktopI recommend using flatseal, using this app we can manage permissions of flatpak applications. Example giving permission to ~/Downloads directory to web browsers.
Development Setup
Distrobox
Distrobox is tool that creates a container using podman or docker. We can run any linux distribution in terminal using distrobox container. We will be using ubuntu 22.04 for all our development need. We will install all the necessary tools, softwares and dependencies in distrobox container so that our host fedora silverblue remains clean. Here are the linux distros which you can install as container distros. We have already installed distrobox in the beginning. Now lets create a distrobox container.
Create a distrobox container (ubuntu 22.04):
distrobox create --image docker.io/library/ubuntu:22.04 --name ubuntu-22.04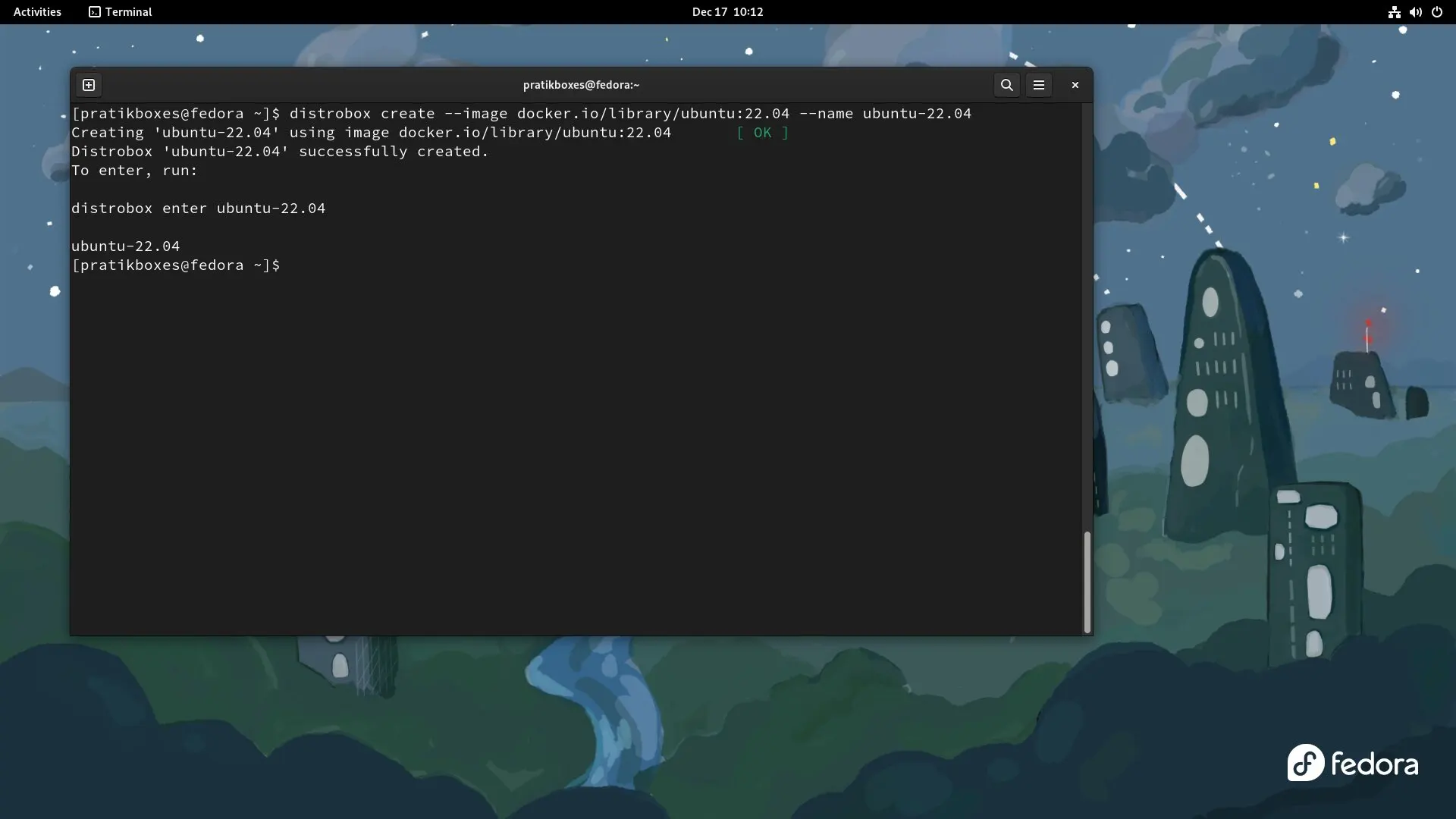
List distrobox containers:
distrobox listEnter the ubuntu distrobox:
distrobox enter ubuntu-22.04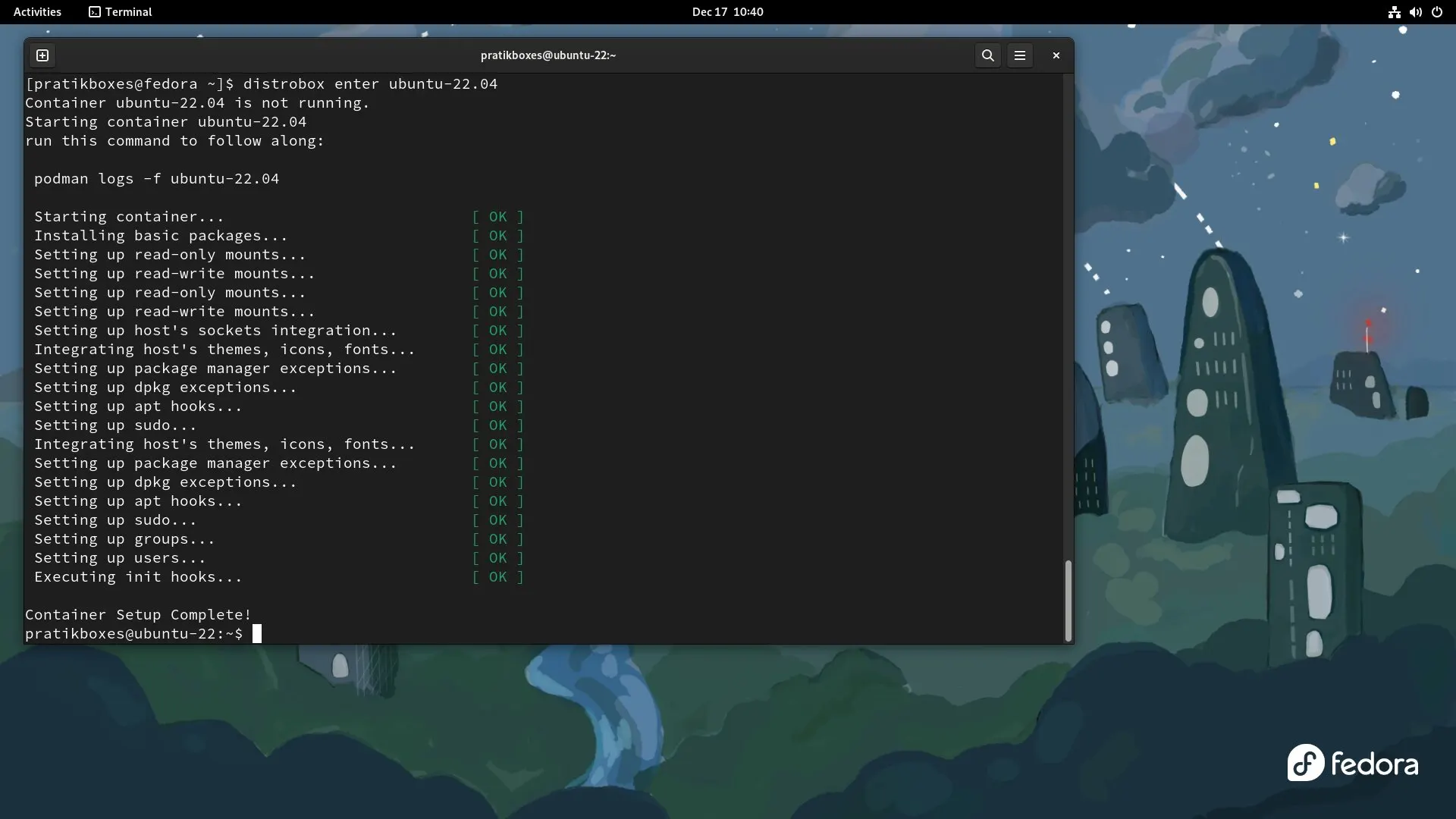
In the above image you can see the shell promt shows ubuntu. We are inside ubuntu distrobox container.
Updating distrobox container (ubuntu-22.04):
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeInstalling version control system git inside ubuntu:
sudo apt install gitWe will be setting some different keyboard shortcuts to open specific terminal shell directly from either our ubuntu-22.04 distrobox or host fedora silverblue in latter part of the blog.
Installing Nodejs
We will be installing Node Version Manager.
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.2/install.sh | bashReload bash:
bashInstalling nodejs LTS:
nvm install --ltsConfirm nodejs installation:
node -vInstalling OpenJDK
Installing Java OpenJDK 11:
sudo apt install openjdk-11-jdkConfirm your installation using:
java -versionInstalling python3-pip
Installing python package manager pip:
sudo apt install python3-pipInstalling Text Editors / IDEs
We will be making a ~/bin directory inside home and we will add this directory path to $PATH so than the binaries inside directory are always availabe to execute.
mkdir ~/binOpen Files(nautilus) app and enable show hidden files. Then open .bashrc with your preferred text editor. Add this in ~/.bashrc to add ~/bin directory to path.
if [ -d "$HOME/bin" ] ;
then PATH="$HOME/bin:$PATH"
fibashrc looks like this:
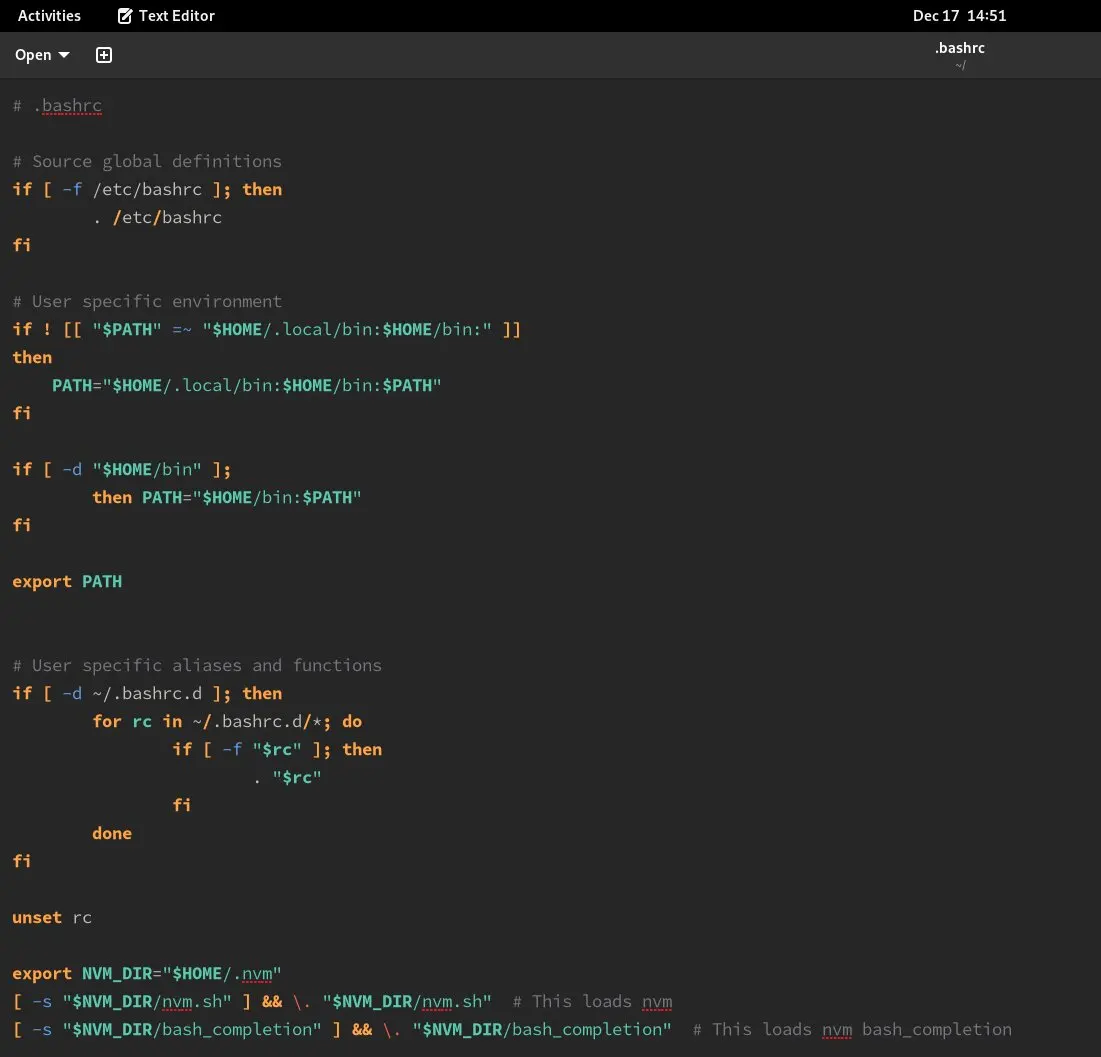
Installing VSCode
Download the .deb file from https://code.visualstudio.com/ Then install vscode using command from within ubuntu distrbox container:
sudo apt install <path of vscode .deb file>We can export the app installed inside ditrobox container to host machine so that the application icon is visible in application menu. Use command distrobox-enter within distrobox container.
distrobox-export --app codeAlso exporting vscode binary:
distrobox-export --app code --bin /usr/bin/code --export-path ~/binInstalling Neovim
Download the .deb file from https://github.com/neovim/neovim/releases and then install neovim using command from within ubuntu distrobox container
sudo apt install <path of neovim .deb file>Now we will export neovim from distrobox container to host Fedora Silverblue. Run this distrobox-export command from within container:
distrobox-export --app nvimAlso exporting nvim binary:
distrobox-export --app nvim --bin /usr/bin/nvim --export-path ~/binInstalling vim plug plugin manager for neovim.
sh -c 'curl -fLo "${XDG_DATA_HOME:-$HOME/.local/share}"/nvim/site/autoload/plug.vim --create-dirs \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/junegunn/vim-plug/master/plug.vim'Neovim configuration file is ~/.config/init.vim. You can use my neovim configuration file for reference. Open neovim and type :PlugInstall to install necessary plugins.
If you want to setup neovim like an IDE using lua config refer these two videos by ThePrimeagen and TJ DeVries.
Podman and Docker
Fedora silverblue comes with podman out of the box. According to official documentation “Podman is a daemonless, open source, Linux native tool designed to make it easy to find, run, build, share and deploy applications using Open Containers”. Podman is better alternative to docker. One difference between podman and docker is that podman can be run as root and non-root users. Also podman does not rely on a daemon like docker. This article has detailed comparison between podman and docker. Since podman comes preinstalled in our host Fedora Silverblue, we can use podman inside our distrobox (ubuntu-22.04) using command
sudo ln -s /usr/bin/distrobox-host-exec /usr/local/bin/podmanBonus
Here are some things that I wanted to share but cannot put in any above categories.
Setting keyboard shortcuts to directly open terminal shell inside our distrobox container
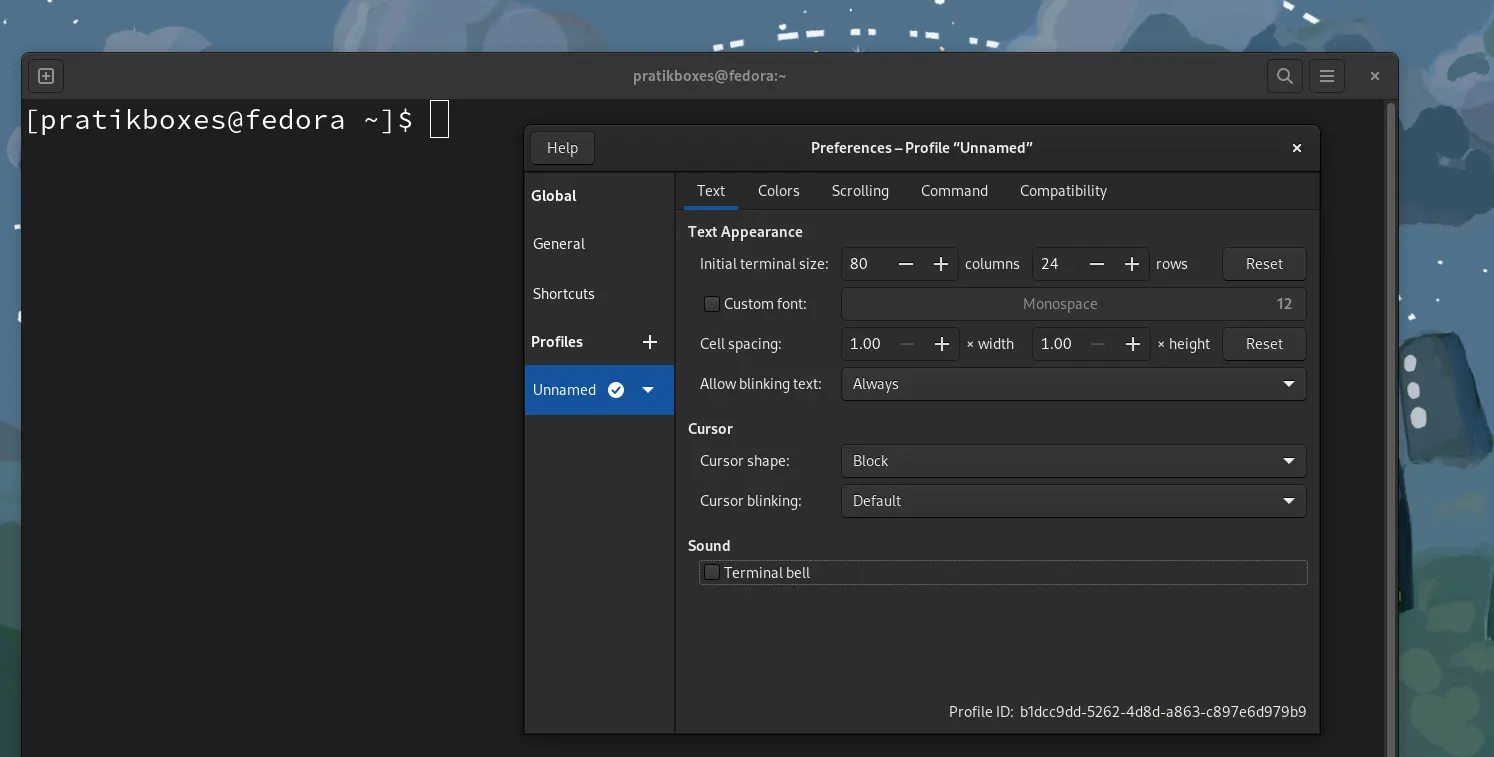
- Open gnome-terminal prefrences. There we be default profile with a check mark and with name “unnamed”, click on the small drop-down button and rename it to something like “Silverblue host”. When we open terminal, it opens in this profile.
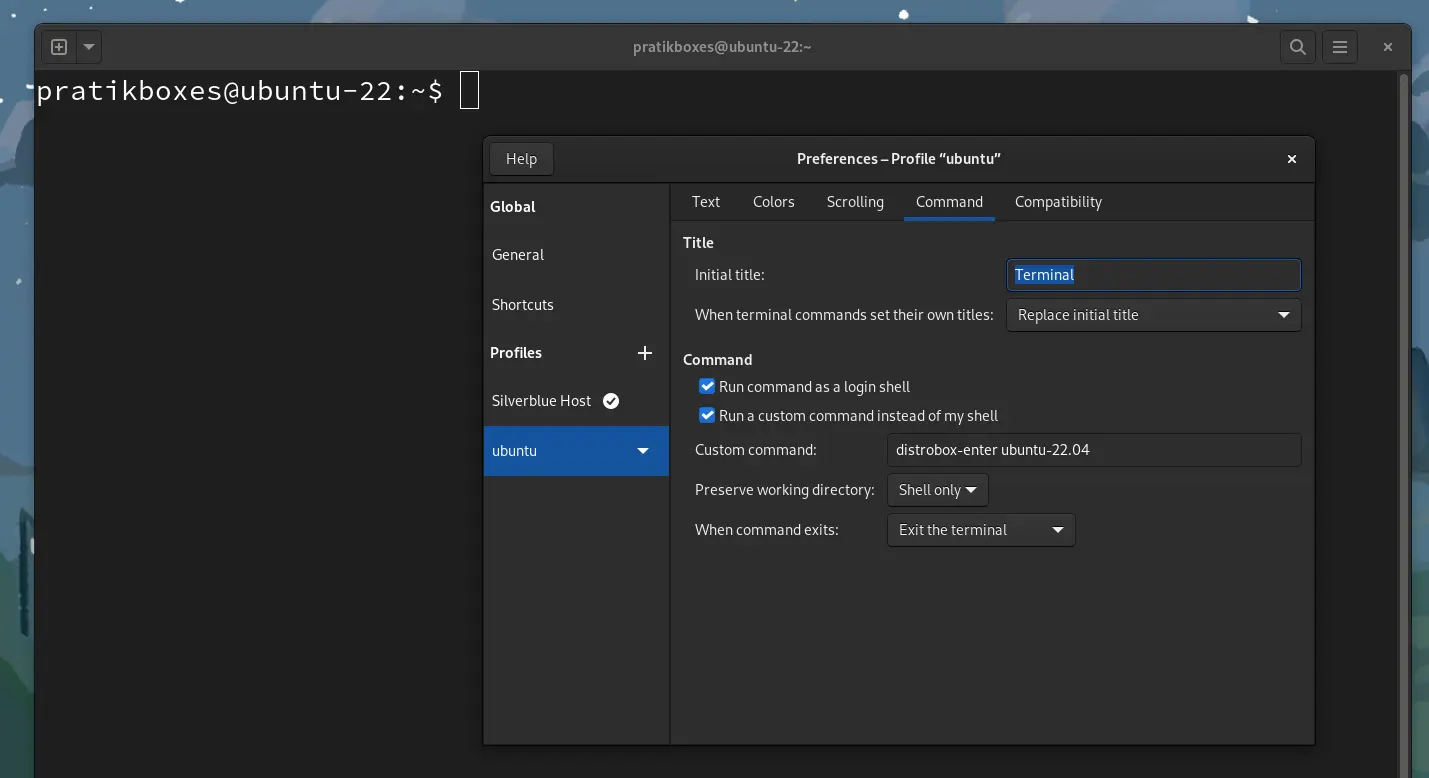
- Then Create a new profile with name “ubuntu”. In the command tab checkmark the two checkboxes. Enter the below command in the “Custom Command field”
distrobox-enter ubuntu-22.04This will make the shell to open inside the distrobox container.
Setting Keyboard shortcuts to open terminal.
In Settings -> Keyboard -> View and Customize Shortcuts -> Custom Shortcuts.
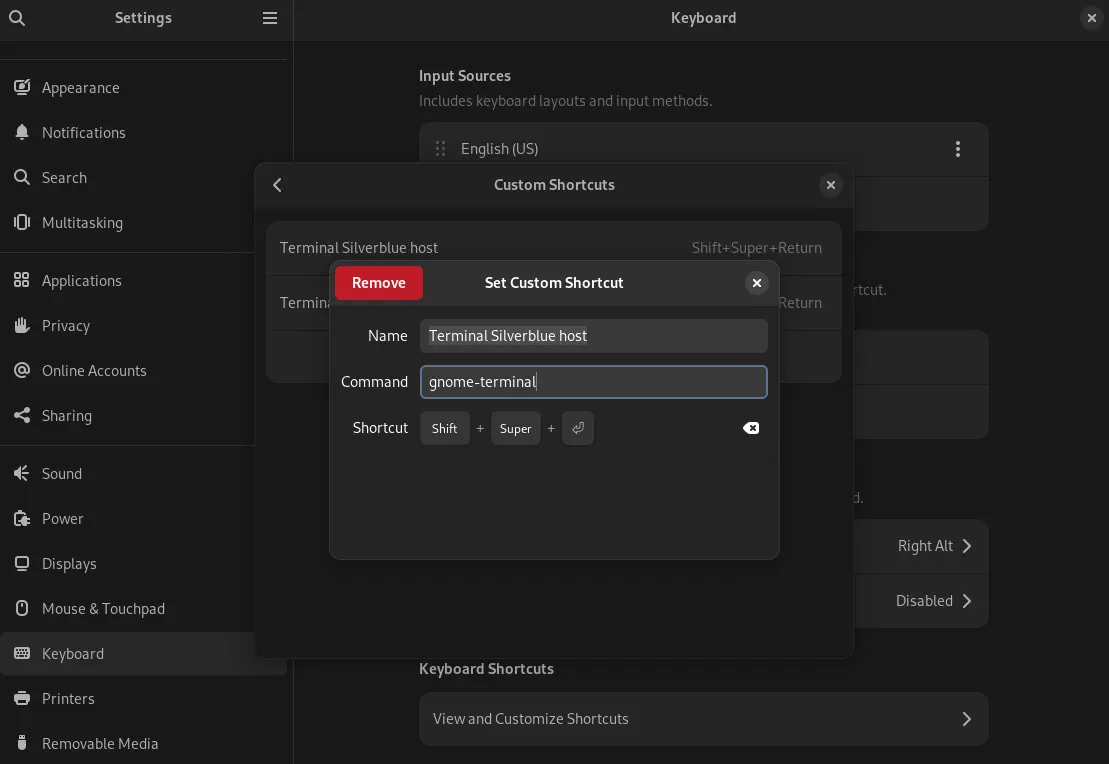
- Setting keyboard shortcut Super + Shift + Enter to open gnome-terminal with default profile i.e. shell will be inside Silverblue host.
- Setting keyboard shortcut Super + Enter to open gnome-terminal with ubuntu profile i.e. the shell will be inside distrobox ubuntu container.
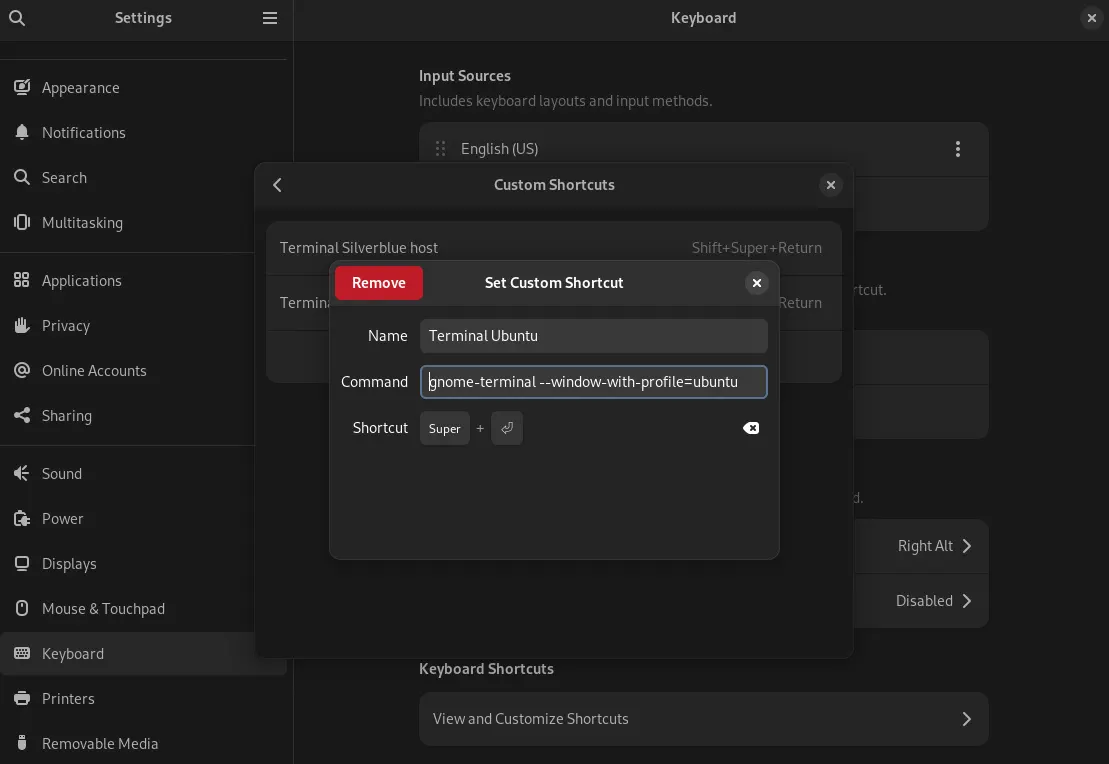 The command gnome-terminal —window-with-profile=ubuntu opens terminal with shell inside distrobox ubuntu container.
The command gnome-terminal —window-with-profile=ubuntu opens terminal with shell inside distrobox ubuntu container.
Updating
Updating everything(fedora, flatpaks and distrobox containers) using one command:
rpm-ostree upgrade && flatpak update -y && distrobox upgrade --allYou can add alias in bashrc
alias update="rpm-ostree upgrade && flatpak update -y && distrobox upgrade --all"Housekeeping
Cleaning old images and Flatpak cache:
rpm-ostree cleanup -b && rpm-ostree cleanup -p && rpm-ostree cleanup -r && sudo rm -rf /var/tmp/flatpak-cache*bash alias:
alias clean="rpm-ostree cleanup -b && rpm-ostree cleanup -p && rpm-ostree cleanup -r && sudo rm -rf /var/tmp/flatpak-cache*"Installing some additional tools
Installing some extra programs that I use daily. Installing gnome-tweaks, imagemagick and ffmpeg inside distrobox ubuntu container.
sudo apt install gnome-tweaks imagemagick ffmpegExporting these applications to host system:
distrobox-export --app gnome-tweaks &&
distrobox-export --app convert --bin /usr/bin/convert --export-path ~/bin/ &&
distrobox-export --app mogrify --bin /usr/bin/mogrify --export-path ~/bin/ &&
distrobox-export --app ffmpeg --bin /usr/bin/ffmpeg --export-path ~/bin/Some useful bash alias
alias ll='ls -la'
alias la='ls -a'
alias docker='podman'
alias mkdir='mkdir -pv'
alias suspend='systemctl suspend'
alias cp="cp -i"
alias mv='mv -i'
alias rm='rm -i'
alias grep='grep --color=auto'
alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
alias fgrep='fgrep --color=auto'
alias df='df -h'For more bash alias you can refer these two videos Let’s Share Our Favorite Bash Aliases and Shell Aliases Every Linux User Needs from Distrotube.
Conclusion
That sums up everything. I usually update and do housekeeping of my system once every week. So I run commands update and clean for which I have alias in bashrc. I also did a major upgrade from Fedora 36 to 37 for which I had to reinstall firefox firefox-langpacks, gnome-software and gnome-software-rpm-ostree. Everything else works like a charm no issues yet. I also wanted to take a look at opensuse micro os which is also immutable and comes with distrobox and flathub out of the box. Thankyou for reading this blog I hope this helped you and please feel free to provide feedback and constructive critisism on my socials.